Account and Transaction API Specification - v2.0.0
Version Control
| Version | Date | Author | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0.0 draft-0.0.1 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | This is the initial draft version. | |
| 2.0.0 draft-0.0.2 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Updated draft. | |
| 2.0-draft-3 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Updated draft. Removed all common elements | |
| 2.0-rc1 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Incorporate PCA and BCA Data model changes Account type related changes | |
| 2.0-rc2 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Account and Transaction Info API restructure. Section 4.6 - Removed rate limiting, and clarification on behaviour. Updates:
| |
| 2.0-rc3 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | This is the initial draft version for rc3 Updates:
| |
| 2.0.0 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | This is the baseline version. No changes from v2.0-rc3. |
Overview
This specification describes the Account Information and Transaction API flows and payloads.
The API endpoints described here allow an Account Information Service Provider ('AISP') to:
- Register an intent to retrieve account information by creating an "account request". This registers the data "permissions", expiration and historical period allowed for transactions / statements - that the customer (PSU) has consented to provide to the AISP; and
- Subsequently retrieve account and transaction data.
This specification should be read in conjunction with Read/Write Data API Specification v2.0 which provides a description of the elements that are common across all the Read/Write Data APIs.
Document Structure
This document consists of the following parts:
Overview: Provides an overview of the scope of the API and the key decisions and principles that contributed to the specification.
Basics: The section identifies the resources, operations that are permitted on those resources, and various special cases.
Endpoints: Provides the list of endpoints for the API specification. The individual end-points are documented in seperate pages along with the data model that the employ and usage examples.
Security & Access Control: Specifies the means for AISPs and PSUs to authenticate themselves and provide consent.
Data & Payloads: Documents data structures and data architecture that applies to all the end-points. End-point specific data structures are documented in seperate pages along with the end-points that employ the data structure.
Swagger Specifications: Provides links to the swagger specifications for the APIs.
Scope
The APIs specified in this document provide the ability for AISPs to access a PSU's account and transaction information for domestic PSD2 in-scope accounts.
The only resource that specifically relates to the CMA Order is the products resource - with the BCA and PCA objects. All other resources are driven by PSD2 requirements.
Out of Scope
This Account and Transaction Info API specification does not cater for:
- Write operations (the ability to create) standing orders, direct debits and beneficiaries.
- Progressive or changing consent - if the consent between the AISP and PSU changes, then the existing account-request object is deleted and a new account-request is created with the new consent/authorisation details.
- The ability for the AISP to pre-specify the list of accounts that have been agreed with the PSU for consent/authorisation.
- Multi-authentication flows have been designed - but the full implications of the multi-authentication flows have not been worked through - so these are not included in this version.
- Non-functional requirements and specification of caching and throttling.
Basics
Overview
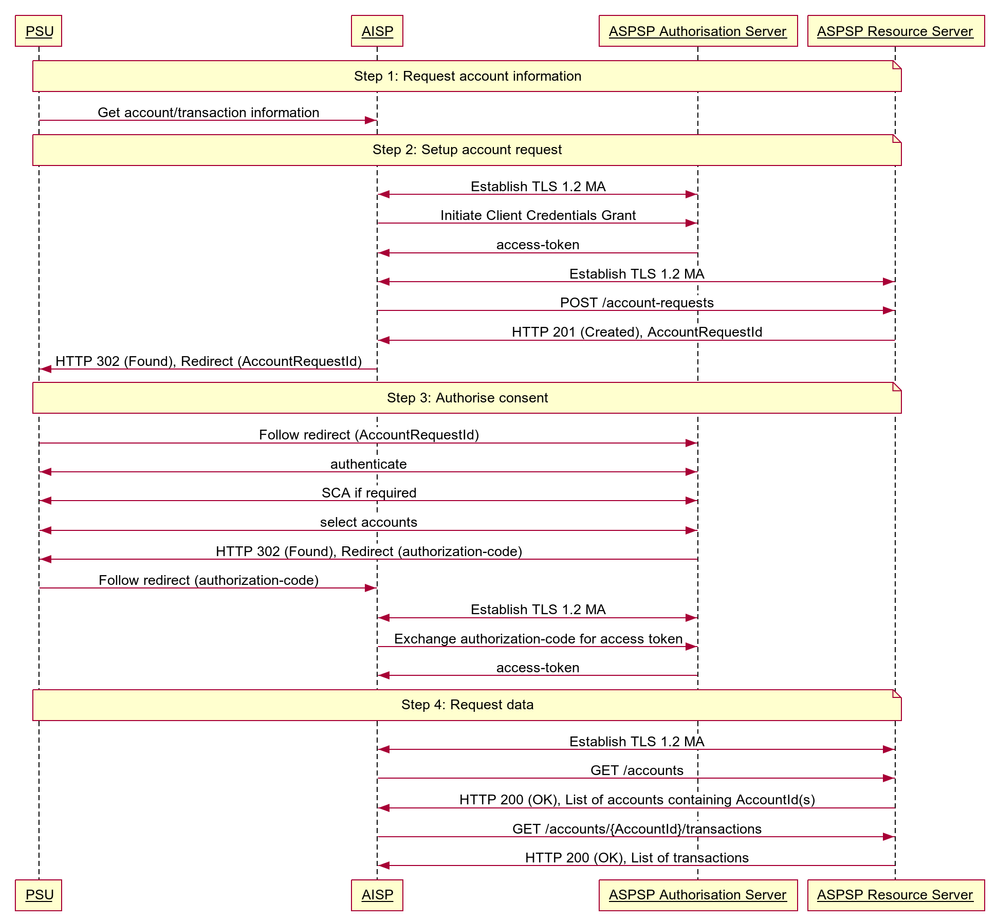
The figure below provides a general outline of an account information requests and flow using the Account Info APIs.
Steps
Step 1: Request Account Information
- This flow begins with a PSU consenting to allow an AISP to access account information data.
Step 2: Setup Account Request
- The AISP connects to the ASPSP that services the PSU's account(s) and creates an account-request resource. This informs the ASPSP that one of its PSUs is granting access to account and transaction information to an AISP. The ASPSP responds with an identifier for the resource (the AccountRequestId - which is the intent identifier). This step is carried out by making a POST request to /account-requests endpoint.
- The account-request resource will include these fields - which describe the data that the PSU has consented with the AISP:
- Permissions - a list of data clusters that have been consented for access
- Expiration Date - an optional expiration for when the AISP will no longer have access to the PSU's data
- Transaction Validity Period - the From/To date range which specifies a historical period for transactions and statements which may be accessed by the AISP
- An AISP may be a broker for data to other parties, and so it is valid for a PSU to have multiple account-requests for the same accounts, with different consent/authorisation parameters agreed.
Step 3: Authorise Consent
- The AISP redirects the PSU to the ASPSP. The redirect includes the AccountRequestId generated in the previous step. This allows the ASPSP to correlate the account-request that was setup. The ASPSP authenticates the PSU. The ASPSP updates the state of the account-request resource internally to indicate that the account request has been authorised.
- The principle we have agreed is that consent is managed between the PSU and the AISP - so the account-request details must not be changed (with the ASPSP) in this step. The PSU will only be able to authorise or reject the account-request details in its entirety.
- During authorisation - the PSU selects accounts that are authorised for the AISP request (in the ASPSP's banking interface).
- The PSU is redirected back to the AISP.
Step 4: Request Data
- This is carried out by making a GET request the relevant resource.
- The unique AccountId(s) that are valid for the account-request will be returned with a call to GET /accounts. This will always be the first call once an AISP has a valid access token.
Sequence Diagram
Idempotency
The API endpoints for creating account-request resources are not idempotent.
If a time-out error occurs - then we would expect an AISP to create a new account-request resource - rather than try with the same resource.
Endpoints
This section looks at the list of available API endpoints to access Account Information and Transaction data and optionality (definitions of mandatory, conditional or optional are defined in the Principles section).
If an ASPSP has not implemented an API endpoint, it must respond with a 404 (Not Found) for requests to that URL.
Endpoint design considerations:
- Having resources that are finer grained (e.g., beneficiaries, direct-debits, standing-orders) means that we can, in the future, manage these resources (with unique identifiers)
- While balances is not a typical resource - we believe having an /accounts/{AccountId}/balances endpoint is simpler to understand than a URI to expand the /accounts resource
- Some ASPSPs were uncomfortable implementing the bulk APIs (e.g., /accounts, /transactions, /beneficiaries etc.) - so the bulk APIs have been specified as optional. However - the bulk endpoint for /accounts is mandatory to discover what accounts have been authorised for the account-request.
We have specified the "mandatory" endpoints for the functioning of the Account Info APIs.
However, endpoints will be not be "mandatory" if ASPSPs do not provide these resources via existing online channels - e.g., direct debits, standing orders, statements.
Security & Access Control
Scopes
The access tokens required for accessing the Account Info APIs must have at least the following scope:
accounts
Grants Types
AISPs must use a client credentials grant to obtain a token to access the account-requests resource.
AISPs must use an authorization code grant to obtain a token to access all other resources.
Consent Authorisation
The AISP must create an account-request resource through a POST operation. This resource indicates the consent that the AISP claims it has been given by the PSU to retrieve account and transaction information. At this stage, the consent is not yet authorised as the ASPSP has not yet verified this claim with the PSU.
The ASPSP responds with an AccountRequestId. This is the intent-id that is used when initiating the authorization code grant (as described in the Trust Framework).
As part of the authorization code grant:
- The ASPSP authenticates the PSU.
- The ASPSP plays back the consent (registered by the AISP) back to the PSU - to get consent authorisation. The PSU may accept or reject the consent in its entirety (but not selectively).
- The ASPSP presents the PSU a list of accounts to which the consent will apply.
Once these steps are complete, the consent is considered to have been authorised by the PSU.
Consent Elements
The Account Request resource consists of the following fields, which together form the elements of the consent provided by the PSU to the AISP:
- Permissions: The set of data clusters that the PSU has consented to allow the AISP to access
- ExpirationDateTime: The date-time up to which the consent is valid.
- TransactionFromDateTime: The earliest point of the transaction / statement historical period that the PSU has consented to provide access to the AISP.
- TransactionToDateTime: The last point of the transaction / statement historical period that the PSU has consented to provide access to the AISP.
Permissions
Permissions codes will be used to limit the data that is returned in response to a resource request.
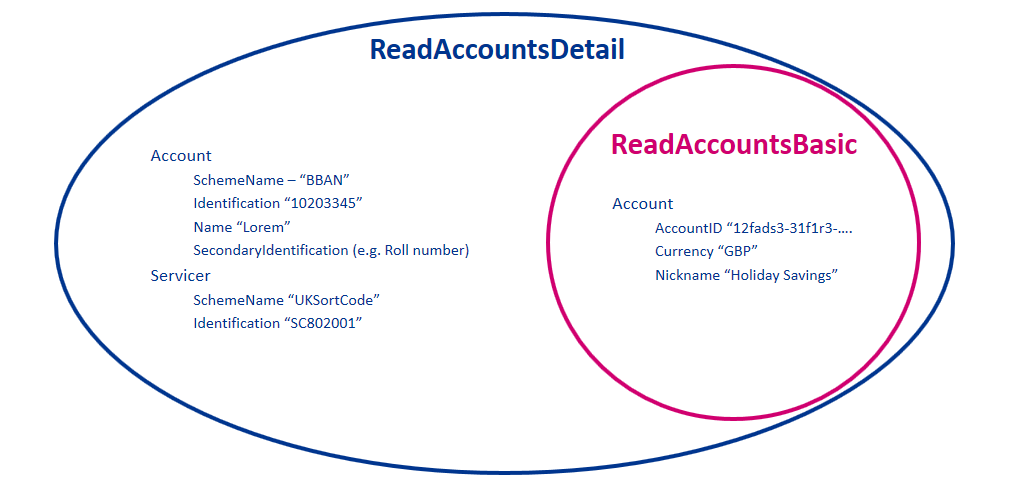
When a permission is granted for a "Detail" permission code (e.g., ReadAccountsDetail), it implies that access is also granted to the corresponding "Basic" permission code (e.g., ReadAccountsBasic)
The permissions array must contain either ReadAccountsBasic or ReadAccountsDetail.
The following combinations of permissions are not allowed, and the ASPSP must reject these account-requests with a 400 response code:
- Account requests with an empty Permissions array
- Account requests with a permission code that is not supported by the ASPSP (ASPSPs are expected to publish which API endpoints are supported)
- Account requests with a Permissions array that contains ReadTransactionsBasic but does not contain at least one of ReadTransactionsCredits and ReadTransactionsDebits.
- Account requests with a Permissions array that contains ReadTransactionsDetail but does not contain at least one of ReadTransactionsCredits and ReadTransactionsDebits.
- Account requests with a Permissions array that contains ReadTransactionsCredits but does not contain at least one of ReadTransactionsBasic and ReadTransactionsDetail.
- Account requests with a Permissions array that contains ReadTransactionsDebits but does not contain at least one of ReadTransactionsBasic and ReadTransactionsDetail.
| Permissions | Endpoints | Business Logic | Data Cluster Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ReadAccountsBasic | /accounts /accounts/{AccountId} | Ability to read basic account information | |
| ReadAccountsDetail | /accounts /accounts/{AccountId} | Access to additional elements in the payload | Ability to read account identification details |
| ReadBalances | /balances /accounts/{AccountId}/balances | Ability to read all balance information | |
| ReadBeneficiariesBasic | /beneficiaries /accounts/{AccountId}/beneficiaries | Ability to read basic beneficiary details | |
| ReadBeneficiariesDetail | /beneficiaries /accounts/{AccountId}/beneficiaries | Access to additional elements in the payload | Ability to read account identification details for the beneficiary |
| ReadDirectDebits | /direct-debits | Ability to read all direct debit information | |
| ReadStandingOrdersBasic | /standing-orders /accounts/{AccountId}/standing-orders | Ability to read basic standing order information | |
| ReadStandingOrdersDetail | /standing-orders /accounts/{AccountId}/standing-orders | Access to additional elements in the payload | Ability to read account identification details for beneficiary of the standing order |
| ReadTransactionsBasic | /transactions /accounts/{AccountId}/transactions | Permissions must also include at least one of:
| Ability to read basic transaction information |
| ReadTransactionsDetail | /transactions /accounts/{AccountId}/transactions | Access to additional elements in the payload Permissions must also include at least one of
| Ability to read transaction data elements which may hold silent party details |
| ReadTransactionsCredits | /transactions /accounts/{AccountId}/transactions | Access to credit transactions. Permissions must also include one of:
| Ability to read only credit transactions |
| ReadTransactionsDebits | /transactions /accounts/{AccountId}/transactions | Access to debit transactions. Permissions must also include one of:
| Ability to read only debit transactions |
| ReadStatementsBasic | /statements /accounts/{AccountId}/statements | Ability to read basic statement details | |
| ReadStatementsDetail | /statements /accounts/{AccountId}/statements/{StatementId}/file | Access to additional elements in the payload Access to download the statement file (if the ASPSP makes this available). | Ability to read statement data elements which may leak other information about the account |
| ReadProducts | /products /accounts/{AccountId}/product | Ability to read all product information relating to the account | |
| ReadOffers | /offers /accounts/{AccountId}/offers | Ability to read all offer information | |
| ReadParty | /accounts/{AccountId}/party | Ability to read party information on the account owner. | |
| ReadPartyPSU | /party | Ability to read party information on the PSU logged in. | |
| ReadScheduledPaymentsBasic | /scheduled-payments /accounts/{AccountId}/scheduled-payments | Ability to read basic statement details | |
| ReadScheduledPaymentsDetail | /scheduled-payments /accounts/{AccountId}/scheduled-payments | Access to additional elements in the payload | |
| ReadPAN | All API endpoints where PAN is available as a structured field | Request to access to PAN in the clear | Request to access PAN in the clear across the available endpoints. If this permission code is not in the account-request, the AISP will receive a masked PAN. While an AISP may request to access PAN in the clear, an ASPSP may still respond with a masked PAN if:
|
Detail Permissions
The additional elements that are granted for "Detail" permissions are listed in this section.
All other fields (other than these fields listed) are available with the "Basic" Permission access.
| Permission - Detail Codes | Data Element Name | Occurrence | XPath |
|---|---|---|---|
| ReadAccountsDetail | Account | 0..1 | OBReadAccount2/Data/Account/Account |
| ReadAccountsDetail | Servicer | 0..1 | OBReadAccount2/Data/Account/Servicer |
| ReadBeneficiariesDetail | CreditorAgent | 0..1 | OBReadBeneficiary2/Data/Beneficiary/CreditorAgent |
| ReadBeneficiariesDetail | CreditorAccount | 0..1 | OBReadBeneficiary2/Data/Beneficiary/CreditorAccount |
| ReadStandingOrdersDetail | CreditorAgent | 0..1 | OBReadStandingOrder2/Data/StandingOrder/CreditorAgent |
| ReadStandingOrdersDetail | CreditorAccount | 0..1 | OBReadStandingOrder2/Data/StandingOrder/CreditorAccount |
| ReadTransactionsDetail | TransactionInformation | 0..1 | OBReadTransaction2/Data/Transaction/TransactionInformation |
| ReadTransactionsDetail | Balance | 0..1 | OBReadTransaction2/Data/Transaction/Balance |
| ReadTransactionsDetail | MerchantDetails | 0..1 | OBReadTransaction2/Data/Transaction/MerchantDetails |
| ReadTransactionsDetail | CreditorAccount | 0..1 | OBReadTransaction2/Data/Transaction/CreditorAccount |
| ReadTransactionsDetail | DebtorAccount | 0..1 | OBReadTransaction2/Data/Transaction/DebtorAccount |
| ReadStatementsDetail | StatementAmount | 0..* | OBReadStatement1/Data/Statement/StatementAmount |
| ReadScheduledPaymentsDetail | CreditorAgent | 0..1 | OBReadScheduledPayment1/Data/ScheduledPayment/CreditorAgent |
| ReadScheduledPaymentsDetail | CreditorAccount | 0..1 | OBReadScheduledPayment1/Data/ScheduledPayment/CreditorAccount |
In addition the ReadStatementsDetail is required to access the statement file download via: /accounts/{AccountId}/statements/{StatementId}/file
Example behaviour of the Permissions for the ReadAccountsBasic and ReadAccountsDetail codes is as follows:
Reversing Entries
It is expected that transactions will be returned in the payload irrespective of whether they are reversing entries as long as the PSU has provided consent for that type of transaction.
If the PSU has provided permission for ReadTransactionsCredits, the ASPSP must include all credits including debit reversals.
If the PSU has provided permission for ReadTransactionsDebits, the ASPSP must include all debits including credit reversals.
Expiration Date Time
The ExpirationDateTime is an optional field which specifies the expiration for AISP access to the PSU's data.
The field is optional - as the consent for AISP access to a PSU's data may be indefinite. The ExpirationDateTime is different to the RTS requirement for a PSU to re-authorise after 90 days - which is clarified in the "RTS and SCA Exemptions" section. The same account-request resource will be re-authenticated - with the same ExpirationDateTime as the original request.
The ExpirationDateTime applies to all Permissions (data clusters) being consented.
Transaction To/From Date Time
The TransactionToDateTime and the TransactionFromDateTime specify the period for consented transaction and/or statement history. Both the fields are optional and one may be specified without the other.
The AISP must be restricted to accessing transactions within this period when accessing the transactions resource.
The AISP must be restricted to accessing statements which are completely within this period when accessing the statements resource.
Account Request Status
The Account Request resource may have one of the following status codes after authorisation has taken place:
| Status | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Authorised | The account request has been successfully authorised. |
| 2 | Rejected | The account request has been rejected. |
| 3 | Revoked | The account request has been revoked via the ASPSP interface. |
Consent Revocation
A PSU may revoke consent for accessing account information at any point in time.
A PSU may revoke authorisation directly with the ASPSP. The mechanisms for this are in the competitive space and are up to each ASPSP to implement in the ASPSP's banking interface. If the PSU revokes authorisation with the ASPSP, the Status of the account-request resource must be set to Revoked.
The PSU may request the AISP to revoke consent that it has authorised. If consent is revoked with the AISP:
- The AISP must cease to access the APIs at that point
- The AISP must call the DELETE operation on the account-request resource (before confirming consent revocation with the PSU) to indicate to the ASPSP that the PSU has revoked consent
Changes to Selected Account(s)
The PSU must select the accounts to which the consent should be applied at the point of consent authorisation.
Subsequent changes to the set of accounts to which the consent authorisation applies may be carried out directly with the ASPSP. The method for doing this lies in the competitive space and is not part of this specification.
Additionally, the set of selected accounts may also change due to external factors. This includes (but is not limited to):
- The account being closed.
- The PSU's mandate to operate the account is revoked.
- The account is barred or frozen.
In such a situation, only the affected account is removed from the list of selected accounts. The ASPSP must not revoke authorisation to other accounts.
Risk Scoring Information
Information for risk scoring and assessment will come via:
- FAPI HTTP headers. These are defined in Section 6.3 of the FAPI specification and in the Headers section above.
- Additional fields identified by the industry as business logic security concerns - which will be passed in the Risk section of the payload in the JSON object.
No fields for business logic security concerns have been identified for the Account Info APIs.
Data Model
Using Meta to identify Available Transaction Period
For Accounts & Transaction APIs, the Meta section in API responses may contain two additional fields to indicate the date range for which data has been returned.
The transactions or statements for a particular range of dates may be excluded from the response because:
- The ASPSP does not provide historical transactions / statements for that date range.
- The PSU has not consented to transactions / statements for that date range.
The absence of transactions / statements in the payload does not indicate that there were no transactions / statements during that period.
To ensure that the data is interpreted correctly, the ASPSP may provide the date of the first available transaction and last available transaction as part of the response in the Meta section in the FirstAvailableDateTime and LastAvailableDateTime fields.
"Meta": {
"TotalPages": 1,
"FirstAvailableDateTime": "2017-05-03T00:00:00+00:00",
"LastAvailableDateTime": "2017-12-03T00:00:00+00:00"
}
Mapping to Schemes & Standards
The Account Info API resources, where possible, have been borrowed from the ISO 20022 camt.052 XML standard. However - has been adapted for APIs based as per our design principles.
Deviations from the camt.052 XML standard are:
- The camt.052 header section and trailer sections have been removed - as these are not required for a RESTful API
- Resources have been identified, and payload structures have been designed for these resources - rather than a full message (i.e., camt.052) that encompasses all resources in a report format. This has meant we've designed separate endpoints and payloads to cover:
- accounts
- balances
- beneficiaries
- direct-debits
- offers
- party
- products
- standing-orders
- statements
- transactions
- scheduled-payments
- New payloads have been designed for beneficiaries, direct-debits, standing-orders, and products resources - as these are not in the ISO 20022 standard (or the camt.052 message)
- A DateTime element has been used instead of a complex choice element of Date and DateTime (across all API endpoints). Where time elements do not exist in ASPSP systems - the expectation is the time portion of the DateTime element will be defaulted to 00:00:00+00:00
- Variations for the accounts structure include:
- Standardised inline with the Payment API account structures
- Contains elements to identify an account Nickname, SecondaryIdentification
- Variations for the balances structure include:
- Adding a Type into the CreditLine section - to allow for multiple credit line types affecting the available balance
- DateTime element has been specified instead of a complex choice of Date and DateTime
Variations for the transactions structure include:
Renaming "entry" to "transaction" for consistency - as this is the language used in the CMA Order, and PSD2
DateTime elements used instead of a complex choice of Date and DateTime
Flattening of the structure for BankTransactionCode and ProprietaryBankTransactionCode
Additional information for an AddressLine, MerchantDetails, and a running Balance
Resources
Each of the Account and Transaction API resources are documented in sub-pages of this specification. Each resource is documented with:
- Endpoints
- The API endpoints available for the resource
- Data Model
- Resource definition
- UML diagram
- Permissions as they relate to accessing the resource
- Data dictionary - whcih defines fields, re-usable classes, mandatory (1..1) or conditional (0..1) as defined in the Design Principles section, and enumerations
- Usage Examples
Swagger Specification
The Swagger Specification for Account Information APIs can be downloaded from the following links:
- JSON:
- YAML:
© Open Banking Limited 2019 | https://www.openbanking.org.uk/open-licence | https://www.openbanking.org.uk