Open Banking Security Profile - Implementer's Draft v1.1.1
Version Control
Version | Date | Author | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1.0.0 |
| Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Published |
| Implementer's Draft v1.0.0 |
| Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Renamed to Implementer's Draft. Client Registration section moved to OB Directory Specification |
| Implementer's Draft v1.0.1 |
| Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Recreating document from up to date sub sections. Clarifications to Implementation Guide
|
| Implementer's Draft v1.1.0 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Reflecting changes to the R/W API specifications for v1.1:
| |
| Implementer's Draft v1.1.1 | Open Banking Read/Write API Team | Clarification to reflect that TPPs are NOT required to pass ACR values in either the requested acr_values string or inside the request object to address a possible mis-interpretation. This is a MAY and not a MUST as already stated in v1.1.0 of the specification. |
UK Open Banking OIDC Security Profile
Introduction
In many cases, Fintech services such as aggregation services use screen scraping and store user passwords. This model is both brittle and insecure. To cope with the brittleness, it should utilize an API model with structured data and to cope with insecurity, it should utilize a token model such as OAuth [RFC6749, RFC6750].
Financial API aims to rectify the situation by developing a REST/JSON model protected by OAuth. However, just asking to use OAuth is too vague as there are many implementation choices. OAuth is a framework which can cover wide range of use-cases thus some implementation choices are easy to implement but less secure and some implementation choices are harder to implement but more secure. Financial services on the internet is a use-case that requires more secure implementation choices. That is, OAuth needs to be profiled to be used in the financial use-cases.
The Open Banking Profile detailed below outlines the differences between the FAPI R+W profile with clauses and provisions necessary to reduce delivery risk for ASPSPs OP
Notational Conventions
The key words "shall", "shall not", "should", "should not", "may", and "can" in this document are to be interpreted as described in ISO Directive Part 2. These key words are not used as dictionary terms such that any occurence of them shall be interpreted as key words and are not to be interpreted with their natural language meanings.
Financial Services – Open Banking API Security Profile
This document is based on the OpenID Foundations Financial API Read+Write specification document which in turn is based on the Read only specification document. The Open Banking profile will further shape these two base profiles in some cases tightening restrictions and in others loosening requirements using key words
5. Read and Write API Security Profile
5.2 OB API Security Provisions
5.2.1 Introduction
Open Banking's API Profile does not distinguish between the security requirements from a technical level between "read" and "write" resources. The security requirements for accessing PSU resources held at ASPSPs requires more protection level than a basic RFC6749 supports.
As a profile of The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework, this document mandates the following to the OpenBanking Financial APIs.
5.2.2 Authorization Server
The Authorization Server
- shall support confidential clients;
- shall not support public clients;
- shall support user authentication at appropriate level as defined in PSD2 be that LoA 3 or 2 or other.
- shall require the
response_typevalues code orcode id_tokenorcode id_token token; - shall authenticate the confidential client at the Token Endpoint using one of the following methods:
- TLS mutual authentication [MTLS] https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-mtls-05; or (Recommended)
- client_secret_basic or client_secret_post provided the client identifier matches the client identifier bound to the underlying mutually authenticated TLS transport session; or (Allowed)
- JWS Client Assertion using the client_secret or a private key as specified in section 9 of [OIDC]; (Recommended)
- shall issue an ID Token in the token response when
openidwas included in the requestedscopeas in Section 3.1.3.3 of OIDC with itssubvalue corresponding to the "Intent Ticket ID" and optionalacrvalue in ID Token. - may support refresh tokens.
Further, if it wishes to provide the authenticated user's identifier to the client in the token response, the authorization server
- shall issue an ID Token in the token response when openid was included in the requested scope as in Section 3.1.3.3 of [OIDC] with its sub value corresponding to the authenticated user and mandatory acr value in ID Token.
- must support Request Objects passed by value as in clause 6.3 of OIDC.
5.2.3 Public Client
Open Banking OPs can support Public Clients at their discretion.
Should an OP wish to support public clients all provisions of the FAPI Read Write API security profile will be adhered too with exceptions below;
- shall request user authentication at appropriate level as defined in PSD2 be that LoA 3 or 2 or other.
5.2.4 Confidential Client
A Confidential Client
- may use separate and distinct Redirect URI for each Authorization Server that it talks to;
- shall support the following methods to authenticate against the Token Endpoint:
- TLS mutual authentication [MTLS]; or
- JWS Client Assertion using the client_secret or a private key as specified in section 9 of [OIDC]; or
- client_secret_basic or client_secret_post provided the client identifier matches the client identifier bound to the underlying mutually authenticated TLS transport session
- shall accept signed ID Tokens;
6. Accessing Protected Resources
6.2 Access provisions
6.2.1 Protected resources provisions
The resource server with the FAPI endpoints
- shall mandate mutually authenticated TLS 1.2 or later as defined in RFC5246 with the usage following the best practice in RFC7525;
- shall verify that the client identifier bound to the underlying mutually authenticated TLS transport session matches the client that the access token was issued to;
6.3 Client provisions
The confidential client supporting this document
shall use mutually authenticated TLS 1.2 or later as defined in RFC5246 with the usage following the best practice in RFC7525;
- shall supply the last time the customer logged into the client in the x-fapi-customer-last-logged-time header where the value is supplied as ** w3c date **, e.g., x-fapi-customer-last-logged-time: Tue, 11 Sep 2012 19:43:31 UTC; and
- shall supply the customer’s IP address if this data is available or applicable in the x-fapi-customer-ip-address header, e.g., x-fapi-customer-ip-address: 198.51.100.119; and
- shall send x-fapi-financial-id whose value is the unique identifier of the financial institution assigned by OpenBanking.
Further, the client
- may supply the customers authentication context reference (ACR) or applicable in the x-fapi-customer-acr header, e.g., x-fapi-customer-acr;
7. Request object endpoint
7.1 Introduction
- OPs may not support request_uri, OIDC Request Object by Reference.
- OPs must support Request Objects passed by value as in clause 6.3 of OIDC.
8. Security Considerations
8.1 TLS Considerations
Since confidential information is being exchanged, all interactions shall be encrypted with TLS/SSL (HTTPS) in accordance with the recommendations in RFC7525. TLS version 1.2 or later shall be used for all communications.
8.2 Message source authentication failure and message integrity protection failure
It is not mandated that the Authorization request and response are authenticated. Use of request object for the Authorization request and returning an ID token in the Authorization response should be considered to provide message source authentication and integrity protection.
8.3 Message containment failure
8.3.1 Authorization request and response
In this document, the authorization request is not encrypted. Thus, it is possible to leak the information contained if the browser was infected with virus, etc.
Authorization response can be encrypted if an ID token is returned as ID tokens can be encrypted.
It is possible to leak the information through the logs if the parameters were recorded in the logs and the access to the logs are compromised. Strict access control to the logs in such cases should be enforced.
8.3.2 Token request and response
It is possible to leak the information through the logs if the parameters were recorded in the logs and the access to the logs are compromised. Strict access control to the logs in such cases should be enforced.
8.3.3 Resource request and response
Care should be taken so that the sensitive data will not be leaked through the referrer.
If the access token is a bearer token, it is possible to exercise the stolen token. Since the access token can be used against multiple URIs, the risk of its leaking is much larger than the refresh token, which is used only against the token endpoint. Thus, the lifetime of the access token should be much shorter than that of the refresh token. Refer to section 16.18 of OIDC for more discussion on the lifetimes of access tokens and refresh tokens.
Security Architecture
OAuth 2.0, OIDC and FAPI
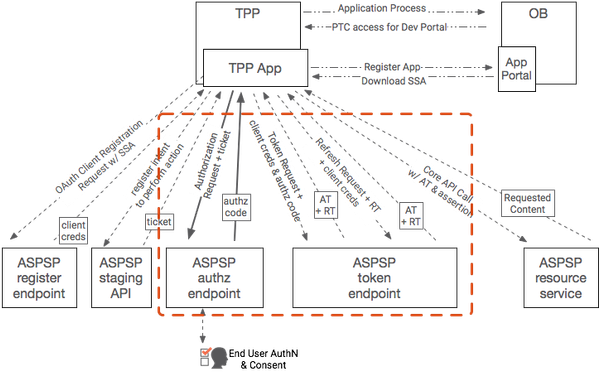
OAuth 2.0 will be the foundational framework for API Security in OpenBanking. The process of requesting a token is standards based - the question is, which standards. OAuth 2.0 itself is a framework which can be deployed in many ways, some of them completely incompatible with financial models. In order to securely use the OAuth 2.0 framework, a profile must exist by which both TPP and ASPSP participants are certified to have correctly configured their clients and servers. The Financial API working group in the OpenID Foundation has created a draft standard for configuration of financial grade API security regimes, and it is strongly recommended that OpenBanking follow that standard. If any FAPI-compliant vendor can participate in the OpenBanking ecosystem, it means that vendors can work to the standard and reach many customers, rather than having to create different solutions for different banking platforms.
Consuming PSU owned Resources from an ASPSP
Overview
See: http://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#JWTRequests (OpenID Connect Core Section 6)
The OpenID Connect Request object uses exactly the same claims object for specifying claim names, priorities, and values, however if the request object is used, the claims object becomes a member in an assertion that can be signed and encrypted, allowing the ASPSP to authenticate the request from the TPP and ensure it hasn't been tampered with. The OpenID Connect request object can either be passed as a query string parameter, or can be referenced at an endpoint that could theoretically be protected by MATLS. OpenBanking, in conjuction with major IAM vendors, is ruling out the use of JWT Request objects by reference due a number of delivery risks and remaining security concerns.
In addition to specifying a ticket, the TPP can optionally require a minimum strength of authentication context or request to know how long ago the user was actually authenticated. Multiple tickets could be passed if necessary. Everything is fully specified. Vendors who implement this feature are not creating a one-off proprietary feature, they are simply supporting the OpenID Connect standard.
Full accountability is available as required by all participants. Not only can the ASPSP prove that they received the original request from the TPP, but the TPP can prove that the access token that comes back was the token that was intended to be affiliated to this specific payment.
Hybrid Flow Request with Intent Id
This section describes parameters that should be used with an hybrid grant flow request so that an intent id can be passed from the TPP to an ASPSP.
Prior to this step,
- The TPP would have already registered an intent with an ASPSP. This is achieved by using one of the account information or payment initiation APIs.
- The ASPSP would have responsded with an intent id.
Hybrid Grant Parameters
Minimum Conformance
Overview
This section describes the bare minimum set of Authorization Request parameters that an ASPSP must support for the Jan, 2018 release. The technical definitive reference is specified in OpenID Connect Core Errata 1 Section 6.1 (Request Object). All standards and guidance MUST be followed as per the specification.
All ASPSPs MUST support the issuance of OIDC ID Tokens, a TPP MAY request that an ID token is issued.
Parameter | Open Banking | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| response_type | Required | OAuth 2.0 requires that this parameter is provided. Value is set to 'code id_token', 'code id_token token' or 'code' TPPs MUST provide this parameter and set its value to one of the three above depending on what the ASPSP supports as described in its well-known configuration endpoint. The values for these parameters MUST match those in the Request Object, if present. Note: risks have been identified with "code" flow that can be mitigated with hybrid flow, the OpenBanking Profile allows ASPSPs to indicate what grant types are supported using the standard well-known configuration endpoint. RP's must take care in valdiating that code swap attacks have not been attempted. |
| client_id | Required | TPPs MUST provide this value and set it to the client id issued to them by the ASPSP to which the authorization code grant request is being made. |
| redirect_uri | Required | TPPs MUST provide the URI to which they want the resource owner's user agent to be redirected to after authorization. This MUST be a valid, absolute URL that was registered during Client Registration with the ASPSP. |
| scope | Required | TPPs MUST specify the scope that is being requested. At a minimum the scope parameter MUST contain openid The scopes MUST be a sub-set of the scopes that were registered during Client Registration with the ASPSP. |
| state | Recommended | TPPs MAY provide a state parameter. The parameter may be of any format and is opaque to the ASPSP. If the parameter is provided, the ASPSP MUST play-back the value in the redirect to the TPP OPs SHOULD include the s_hash |
| request | Required | The TPP MUST provide a value for this parameter. The parameter MUST contain a JWS that is signed by the TPP. The JWS payload MUST consist of a JSON object cotntaining a request object as per OIDC Core 6.1. The request object MUST contain a claims section that supports as a minimum
Inside an ID Token. The request object MAY contain claims to be retrieved via the UserInfo endpoint only if the endpoint is made available and listed on the well known configuration endpoint on the authorisation server. The request object MAY contain additional claims to be requested should the ASPSPs Authorization Server support them, these claims will be listed on the OID Well Known configuration endpoint. |
Example for minimum conformance
Examples are non-normative
HTTP Request
|
Request JWS (Without Base64 encoding)
Note that "essential" is an optional required OPTIONAL. Indicates whether the Claim being requested is an Essential Claim. If the value is true, this indicates that the Claim is an Essential Claim. For instance, the Claim request:
"auth_time": {"essential": true}
can be used to specify that it is Essential to return an auth_time Claim Value.If the value is false, it indicates that it is a Voluntary Claim. The default is false.By requesting Claims as Essential Claims, the RP indicates to the End-User that releasing these Claims will ensure a smooth authorization for the specific task requested by the End-User. Note that even if the Claims are not available because the End-User did not authorize their release or they are not present, the Authorization Server MUST NOT generate an error when Claims are not returned, whether they are Essential or Voluntary, unless otherwise specified in the description of the specific claim. OIDC Core
|
id_token returned - Sub being populated with an EphemeralId of the IntentId - Non Normative
|
id_token returned - Identity Claims and IntentId With sub being populated with an UserIdentifier - Non Normative
|
ID Token Claims Details: Where appropriate please follow the JWT Good Practice Guides http://self-issued.info/docs/draft-sheffer-oauth-jwt-bcp-00.html#rfc.section.3.1
Field | Definition | Notes | Value(s) | Required by | Required by |
iss | Issuer of the token | Token issuer will be specific to the business | Yes | Yes A JSON string that represents the issuer identifier of the authorization server as defined in RFC7519. When a pure OAuth 2.0 is used, the value is the redirection URI. When OpenID Connect is used, the value is the issuer value of the authorization server. | |
sub | Token subject identifier | A unique and non-repeating identifier for the subject i.e the customer.
| Non Identity Services Providers: Use the Intent/Consent ID for this field. Identity Services Providers: Value at the discretion of the OP's. | Yes | Yes |
| openbanking_intent_id | Intent ID of the originating request | A unique and non-repeating identifier containing the intentid. | Use the Intent/Consent ID for this field. | No | Yes - it's acknowledged that this field may duplicate the value in "sub" for many providers. |
| aud | Audience that the ID token is intended for | OpenID Connect protocol mandates thisMUST include the client ID of the TPP. | Should contain the ClientID of the TPP's OAuth Client. | Yes | Yes - as per FAPI RW / OpenID Standard. |
exp | Token expiration date/time | Expressed as an epoch i.e. number of seconds from 1970-01-01T0:0:0Z as measured in UTC. RFC7519. | Yes | Yes The validity length will be at the discretion of the Banks provided that it does not impact the functionality of the APIs. For example, an expiry time of 1 second is insufficient for all Resource Requests. | |
| iat | Token issuance date/time | Expressed as an epoch i.e. number of seconds from | Yes | Yes | |
| auth_time | Date/time when End User was authorised | This field is Required when the max_age request is made or max_age is included as an essential claim. In order to be compliant with the protocol we therefore need to support it. | Expressed as an epoch i.e. number of seconds from 1970-01-01T0:0:0Z as measured in UTC. | Case-specific | Case-Specific |
| nonce | Used to help mitigate against replay attacks | Value is passed in as a Request parameter. If present it must be replayed in the ID token |
| Case-Specific | Required by FAPI Read Write (Hybrid explicitly required - required by OIDC Core for Hybrid Flow). Hybrid Flow support is optional in the OB Security Profile. |
| acr | Authentication Context Class Reference | An identifier that qualifies what conditions the authentication performed satisfied. The acr SHOULD correspond to one of the values requested by the acr_values field on the request however even if not present on the request the aspsp should populate the acr with a value that attests that the aspsp performed or NOT performed an appropriate level of authentication such that the aspsp believes it has met the requirement for "Strong Customer Authentication". | The values to be provided will be to urn:openbanking:psd2:ca or urn:openbanking:psd2:sca. To cover the exemptions cases of PSD2 the PISP / AISP must have a way to request that a Bank NOT perform SCA for some requests. It’s entirely within the banks gift to ignore the requested ACR_VALUES however the Bank must reply with what level of AuthN was performed. (Once RTS comes into affect). | No | Yes Caveated: As RTS is not signed off and will not be delivered by initial go-live aspsps do not have to provide a response value. Aspsps that do not wish to provide this as a claim should remove it from the well-known configuration endpoint. As per OIDC Core, marking a claim as "essential" and an ASPSP can not fulfill it then an error should not be generated. |
amr | Authentication Methods References | The methods that are used in the authentication. For example, this field might contain indicators that a password was supplied or OTP initiated. | Note – industry direction is to consolidate on https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-richer-vectors-of-trust. so expect this field to be replaced shortly. AMR doesn’t give the flexibility to address all the actual particulars of both the authn and the identity that sits behind it. | No | No requirement to specify as it is to be soon superseded by Vectors of Trust. |
| azp | Authorized party | OPTIONAL. Authorized party - the party to which the ID Token was issued. If present, it MUST contain the OAuth 2.0 Client ID of this party. This Claim is only needed when the ID Token has a single audience value and that audience is different than the authorized party. It MAY be included even when the authorized party is the same as the sole audience. The azp value is a case sensitive string containing a StringOrURI value. | OB N/A | No | No specific requirement from OB. |
| s_hash | State Hash Value | May include state hash, s_hash, in the ID Token to protect the state value; | Its value is the base64url encoding of the left-most half of the hash of the octets of the ASCII representation of the state value, where the hash algorithm used is the hash algorithm used in the algHeader Parameter of the ID Token's JOSE Header. For instance, if the alg is HS512, hash the code value with SHA-512, then take the left-most 256 bits and base64url encode them. The s_hashvalue is a case sensitive string. | No | Recommended by OB |
| at_hash | Access Token Hash Value | Access Token hash value. | Its value is the base64url encoding of the left-most half of the hash of the octets of the ASCII representation of the access_token value, where the hash algorithm used is the hash algorithm used in the alg Header Parameter of the ID Token's JOSE Header. For instance, if the alg is RS256, hash the access_token value with SHA-256, then take the left-most 128 bits and base64url encode them. The at_hash value is a case sensitive string. | Conditional | As per Hybrid Flow (OIDC Core) - Yes If the ID Token is issued from the Authorization Endpoint with an access_token value, which is the case for the response_type value code id_token token, this is REQUIRED; otherwise, its inclusion is OPTIONAL. |
| c_hash | Code hash value. | Code Hash Value | Its value is the base64url encoding of the left-most half of the hash of the octets of the ASCII representation of the code value, where the hash algorithm used is the hash algorithm used in the alg Header Parameter of the ID Token's JOSE Header. | Conditional | As per Hybrid Flow (OIDC Core) - Yes. If the ID Token is issued from the Authorization Endpoint with a code, which is the case for the response_type values code id_token and code id_token token, this is REQUIRED; otherwise, its inclusion is OPTIONAL. |
JSON Security Suite Information v1.0
General Guidance for JWT Best Practice: To Be Followed Where Appropriate
http://self-issued.info/docs/draft-sheffer-oauth-jwt-bcp-00.html#rfc.section.3.1
Algorithms to be supported: All Asymmetric Algorithms listed below
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
JWKS Endpoints
All JWKS endpoints will be hosted by OpenBanking Ltd. Upon issuance of a certificate a JWK Set will be created or updated for a given TPP.
All participants should include "kid" and "jku" of the key that was used to sign the payloads. The JKU should be considered a hint only and relying parties should derive and then validate wherever possible the appropriate JWKS endpoint for the message signer.
https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-jose-json-web-signature-41#section-4.1
example:
https://keystore.openbanking.org.uk/tpp/12345678.jwks
As certificates are added and removed by Participant Technical Contacts the jwks endpoint will be updated automatically.
General outline for creating a JWS
Step 1: Select the certificate and private key that will be used for signing the JWS
As the JWS is used for non-repudiation, it MUST be signed using one of JWS issuer's private keys.
The private key MUST have been used by the issuer to get a signing certificate issued from OB.
The signing certificate MUST be valid at the time of creating the JWS.
Step 2: Form the JOSE Header
The JOSE header is a JSON object consisting of three fields (claims):
Claim | RFC 7515 Standard ? | Required ? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| alg | Yes | Mandatory | The algorithm that will be used for signing the JWS. The list of valid algorithms is here https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7518#section-3.1. This MUST be an algorithm that support asymmetric encryption. OB MAY limit this down further. |
| kid | Yes (optional) | Mandatory | The "kid" (key ID) Header Parameter is a hint indicating which key was used to secure the JWS. This MUST match the certificate id of the certificate selected in step 1. The receiver SHOULD use this value to identify the certificate to be used for verifying the JWS. |
Step 3: Form the payload to be signed
The JSON payload to be signed must have the following claims:
Claim | Required ? | Description |
|---|---|---|
| iss | Mandatory | The issuer of the JWS. This MUST match the dn of the certificate selected in step 1. |
The payload to be signed is computed as:
|
Where:
JOSEHeader: is the header created in Step 2 and
json: is the message the original data to be sent
Step 4: Sign and encode the payload
The signed payload is computed as:
|
Where:
privateKey: is the private key selected in step 1
payload: is the payload computed in Step 3
encrypt: Is an encryption function that implements the `alg` identified in Step 2.
Step 5: Assemble the JWS
The JWS is computed as
|
Where:
payload: is the payload computed in Step 3
signedAndEncodedPayload: is the signed element computed in Step 5.
Implementation Guide
Overview
This page provides an implementation perspective of the OB Security Profile aligned to the accepted OB Read/Write APIs for Payments and Accounts Specifications.
Specified Behaviour
The implementation of both the Payments and Accounts API are based on the following known configurations:
Client Types
- As per the OAuth 2.0 specification, the Confidential Client Type is illustrated for both Accounts and Payments API as it has the ability to maintain its own credentials.
Grant Types
OIDC Hybrid Flow (response_type=code id_token)
- Both the Payments and Accounts APIs illustrate the use of request_type=code id_token for the OIDC Hybrid Flow implementation.
- The ASPSP may optionally choose to return Refresh Tokens for the Hybrid Flow when issuing an Access Token
Client Credentials Grant Type using multiple scopes (scope=accounts payments)
- The Client Credentials Grant Type is used across both Payments and Account APIs only when the TPP (AISP/PISP) requires an Access Token (on behalf of itself) in order to access a Payment or Accounts API resource e.g.
Payments:
POST /payments GET /payment-submissions/{PaymentSubmissionId}Accounts:
POST /account-requests
- Where an ASPSP enables the same Confidential Client (ClientId) access to both Payments and Accounts APIs, a TPP may therefore choose to request for either a single scope e.g. accounts or for multiple scope(s) e.g. accounts payments as the TPP may want to use the same Access Token across both APIs.
- Only valid API scopes will be accepted when generating an Access Token (accounts payments).
- Access tokens generated by a Client Credentials grant may not return any refresh tokens (as per the OAuth 2.0 specification)
Access Tokens
- For the Payments and Accounts APIs, the Access Token must be obtained within a Secure, Server Side Context between the TPP (AISP / PISP) and the ASPSP.
- Access Tokens must be validated by the TPP (AISP/PISP) as outlined within the OIDC Errata 1 Specification
Refresh Tokens
- ASPSPs may optionally return a Refresh Token when an Authorization Request is successfully processed at the Token endpoint. The Hybrid flow supports the provisioning of Refresh Tokens.
- The Accounts API implementation below cites an example for AISPs requesting a Refresh Token to refresh an expired Access Token prior to invoking the /accounts resource.
- Refresh Tokens must be validated as outlined in the OIDC Errata 1 Specification
ID Tokens
- ID Tokens must be validated by the TPP (AISP/PISP) as outlined within the OIDC Errata 1 Specification
- TPPs must use the openbanking_intent_id claim to populate and retrieve the IntentID (PaymentID for Payments API and AccountRequestId for the Accounts API) for any required validation.
- The full set of claims that can be represented within an ID Token are documented in the Request Object and ID Token Section of the Security Profile.
Authorization Codes
- Authorization Codes must be validated by the TPP (AISP/PISP) as outlined within the OIDC Errata 1 Specification
Un-Specified Behaviour
The implementation of both the Payments and Accounts API are un-specified for the following configurations:
Client Types
- As per the OAuth 2.0 specification, the Public Client Type has not been illustrated for both Payments and Accounts APIs.
Grant Types
OIDC Hybrid Flow (response_type=code id_token token or response_type=code token)
- Forces an Access Token to be returned from the ASPSP Authorization endpoint (instead of a token endpoint). This is not illustrated in the Payments and Accounts API Specifications.
OIDC Implicit Flow (response_type=id_token token or response_type=id_token)
The Implicit Flow does not authenticate the Client that is invoking the request. This is not illustrated in the Payments and Accounts API Specifications.
Client Credentials Grant Type(scope=openid email profile address phone)
Requesting OIDC specific scopes or any un-specified scopes when using the Client Credentials grant.
Validity Lengths (Authorization Code, Access Token, ID Token, Refresh Token)
These are to be managed in the competitive space; Each ASPSP's Authorization / Resource Server will be configured independently to comply with internal ASPSP Security Policies and Guidelines. The Accounts and Payments API Specifications do not mandate validity lengths.
Authorization Code
OAuth 2.0 Specification suggests an Authorization Code should be short lived to a maximum of 10 minutes. Any codes exceeding this limit to be rejected.
ID Token
ID Token claims (exp and iat) determine its validity.
- Returned with the Authorization Code when the Hybrid flow (code id_token) is initiated.
Access Token
- The expires_in attribute returned by the Authorization Server when an Access Token is generated determines its validity.
- Access Tokens are generally short lived, and where they expire, are then exchanged for another using a longer lived Refresh Token.
- Refer to Section 16.18 of the OIDC Specification - Lifetimes of Access Tokens and Refresh Tokens.
Refresh Token
- The expires_in attribute returned by the Authorization Server when a Refresh Token is generated determines its validity.
- Refresh Tokens are generally longer lived in comparison to Access Tokens.
- Refer to Section 16.18 of the OIDC Specification - Lifetimes of Access Tokens and Refresh Tokens.
Success Flows
Payment API Specification
The sequence diagram below highlights the OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials Grant and OIDC Hybrid flow that are used by the Payments API.
Client Credentials Grant Type (OAuth 2.0)
Summary
This grant type is used by the PISP in Step 2 to setup a single payment with the ASPSP.
- The PISP initiates an Authorization request using valid Client Credentials Grant type and scope(s)
- The ASPSP Authorization Server validates the Client Authentication request from the PISP and generates an Access Token response where the request is valid
- The PISP uses the Access Token to create a new Payment resource against the ASPSP Resource Server
- The ASPSP Resource server responds with the PaymentId for the resource it has created.
- The Client Credentials Grant may optionally be used by the PISP in Step 5 to retrieve the status of a Payment or Payment-Submission where no active Access Token is available.
OIDC Hybrid Flow
Summary
- The Hybrid flow is the recommendation from the OB Security Profile and the FAPI Specification for R/W. The Hybrid flow prevents IdP mixup attacks as documented by Nat Sakimura - Cut and Paste OAuth 2.0 Attack
- This is initiated at the end of Step 2 by the PISP after the PaymentId is generated by the ASPSP and returned to the PISP.
- This is used in a redirect across the PSU and ASPSP in Step 3 in order for the PSU to authorize consent with the ASPSP - for the PISP to proceed with the Payment.
- This is used across the PISP and ASPSP in Step 4 by exchanging the Authorization Code for an Access Token in order to create the Payment-Submission resource.
Non-Normative HTTP Request and Response Examples
Step 1 - Request Payment Initiation
There are no Requests and Responses against the Payments API in this Step for the PSU, PISP and ASPSP.
Step 2 - Setup Single Payment Initiation
1. PISP obtains an Access Token using a Client Credentials Grant Type. The scope payments must be used. When an Access Token expires, the PISP will need to re-request for another Access Token using the same request below.
Request : Client Credentials using private_key_jwt | Response : Client Credentials |
|---|---|
POST /as/token.oauth2 HTTP/1.1
Host: https://authn.alphabank.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Accept: application/json
grant_type=client_credentials
&scope=payments
&client_assertion_type=
urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Aclient-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer
&client_assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRw
czovL2p3dC1pZHAuZXhhbXBsZS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiJtYWlsdG86bWlrZUBleGFtcGxlLmN
vbSIsIm5iZiI6MTQ5OTE4MzYwMSwiZXhwIjoxNDk5MTg3MjAxLCJpYXQiOjE0OTkxODM2MD
EsImp0aSI6ImlkMTIzNDU2IiwidHlwIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9leGFtcGxlLmNvbS9yZWdpc3Rlc
iJ9.SAxPMaJK_wYl_W2idTQASjiEZ4UoI7-P2SbmnHKr6LvP8ZJZX6JlnpK_xClJswAni1T
p1UnHJslc08JrexctaeEIBrqwHG18iBcWKjhHK2Tv5m4nbTsSi1MFQOlMUTRFq3_LQiHqV2
M8Hf1v9q9YaQqxDa4MK0asDUtE_zYMHz8kKDb-jj-Vh4mVDeM4_FPiffd2C5ckjkrZBNOK0
01Xktm7xTqX6fk56KTrejeA4x6D_1ygJcGfjZCv6Knki7Jl-6MfwUKb9ZoZ9LiwHf5lLXPuy
_QrOyM0pONWKj9K4Mj7I4GPGvzyVqpaZUgjcOaZY_rlu_p9tnSlE781dDLuw
Non-Base64 JWT client_assertion {
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": "12345",
"typ": "JWT"
}
.
{
"iss": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"sub": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"exp": 1499187201,
"iat": 1499183601,
"jti": "id123456",
"aud": "https://authn.alphabank.com/as/token.oauth2"
}
.
<<signature>>
| Content-Length: 1103
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Mon, 26 Jun 2017 15:18:28 GMT
{
"access_token": "2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA",
"expires_in": 3600,
"token_type": "bearer",
"scope":"payments"
}
|
2. PISP uses the Access Token (with payments scope) from the ASPSP to invoke the Payments API. This example is sourced directly from the Payment API Specification
| Request : Payments API | Response : Payments API |
|---|---|
POST /payments HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer 2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA
x-idempotency-key: FRESCO.21302.GFX.20
x-fapi-financial-id: OB/2017/001
x-fapi-customer-last-logged-time: 2017-06-13T11:36:09
x-fapi-customer-ip-address: 104.25.212.99
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: application/json
{
"Data": {
"Initiation": {
"InstructionIdentification": "ACME412",
"EndToEndIdentification": "FRESCO.21302.GFX.20",
"InstructedAmount": {
"Amount": "165.88",
"Currency": "GBP"
},
"CreditorAccount": {
"SchemeName": "SortCodeAccountNumber",
"Identification": "08080021325698",
"Name": "ACME Inc",
"SecondaryIdentification": "0002"
},
"RemittanceInformation": {
"Reference": "FRESCO-101",
"Unstructured": "Internal ops code 5120101"
}
}
},
"Risk": {
"PaymentContextCode": "EcommerceGoods",
"MerchantCategoryCode": "5967",
"MerchantCustomerIdentification": "053598653254",
"DeliveryAddress": {
"AddressLine": [
"Flat 7",
"Acacia Lodge"
],
"StreetName": "Acacia Avenue",
"BuildingNumber": "27",
"PostCode": "GU31 2ZZ",
"TownName": "Sparsholt",
"CountySubDivision": [
"Wessex"
],
"Country": "UK"
}
}
}
| HTTP/1.1 201 Created
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Data": {
"PaymentId": "58923",
"Status": "AcceptedTechnicalValidation",
"CreationDateTime": "2017-06-05T15:15:13+00:00",
"Initiation": {
"InstructionIdentification": "ACME412",
"EndToEndIdentification": "FRESCO.21302.GFX.20",
"InstructedAmount": {
"Amount": "165.88",
"Currency": "GBP"
},
"CreditorAccount": {
"SchemeName": "SortCodeAccountNumber",
"Identification": "08080021325698",
"Name": "ACME Inc",
"SecondaryIdentification": "0002"
},
"RemittanceInformation": {
"Reference": "FRESCO-101",
"Unstructured": "Internal ops code 5120101"
}
}
},
"Risk": {
"PaymentContextCode": "EcommerceGoods",
"MerchantCategoryCode": "5967",
"MerchantCustomerIdentification": "053598653254",
"DeliveryAddress": {
"AddressLine": [
"Flat 7",
"Acacia Lodge"
],
"StreetName": "Acacia Avenue",
"BuildingNumber": "27",
"PostCode": "GU31 2ZZ",
"TownName": "Sparsholt",
"CountySubDivision": [
"Wessex"
],
"Country": "UK"
}
},
"Links": {
"Self": "https://api.alphabank.com/open-banking/v1.0/payments/58923"
},
"Meta": {}
}
|
Step 3 - Authorize Consent
1. PISP receives a PaymentId from the ASPSP. The PISP then creates an Authorization request (using a signed JWT Request containing the PaymentID as a claim) for the PSU to consent to the Payment directly with their ASPSP. The request is an OIDC Hybrid flow (requesting for Code and id_token)
Request : OIDC Hybrid Flow | Response : OIDC Hybrid Flow |
|---|---|
Base 64 Encoded Example GET /authorize? response_type=code id_token &client_id=s6BhdRkqt3 &state=af0ifjsldkj &scope=openid payments &nonce=n-0S6_WzA2Mj &redirect_uri=https://api.mytpp.com/cb &request=CJleHAiOjE0OTUxOTk1ODd.....JjVqsDuushgpwp0E.5leGFtcGxlI iwianRpIjoiM....JleHAiOjE0.olnx_YKAm2J1rbpOP8wGhi1BDNHJjVqsDuushgpwp0E Non-Base64 encoded example of the request parameter object {
"alg": "",
"kid": "GxlIiwianVqsDuushgjE0OTUxOTk"
}
.
{
"iss": "https://api.alphabank.com",
"aud": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"response_type": "code id_token",
"client_id": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"redirect_uri": "https://api.mytpp.com/cb",
"scope": "openid payments accounts",
"state": "af0ifjsldkj",
"nonce": "n-0S6_WzA2Mj",
"max_age": 86400,
"claims":
{
"userinfo":
{
"openbanking_intent_id": {"value": "urn:alphabank:intent:58923", "essential": true}
},
"id_token":
{
"openbanking_intent_id": {"value": "urn:alphabank:intent:58923", "essential": true},
"acr": {"essential": true,
"values": ["urn:openbanking:psd2:sca",
"urn:openbanking:psd2:ca"]}}}
}
}
}
.
<<signature>>
|
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location: https://api.mytpp.com/cb#
code=SplxlOBeZQQYbYS6WxSbIA
&id_token=eyJ0 ... NiJ9.eyJ1c ... I6IjIifX0.DeWt4Qu ... ZXso
&state=af0ifjsldkj
|
2. The PSU is then redirected to the PISP. The PISP will now possess the Authorization Code and ID Token from the ASPSP. Note at this point, there is no Access Token. The PISP will now introspect the ID Token and use it as a detached signature to check:
- The hash of the Authorization Code to prove it hasn't been tampered with during redirect (comparing the hash value against the c_hash attribute in ID Token)
- The hash of the State to prove it hasn't been tampered with during redirect (comparing the state hash value against the s_hash attribute in the ID Token)
| Example: ID Token |
|---|
|
3. Once the state and code validations have been confirmed as successful by use of the ID token, the PISP will proceed to obtain an Access Token from the ASPSP using the Authorization Code they now possess. The PISP will present its Authorization Code together with the private_key_jwt. The Access Token is required by the PISP in order to submit the Payment on behalf of the PSU. The payments scope should already be associated with the Authorization Code generated in the previous step.
| Request : Access Token Request using Authorization Code and private_key_jwt | Response : Access Token |
|---|---|
POST /as/token.oauth2 HTTP/1.1
Host: https://authn.alphabank.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Accept: application/json
grant_type=authorization_code
&code=SplxlOBeZQQYbYS6WxSbIA
&redirect_uri=https://api.mytpp.com/cb
&client_assertion_type=
urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Aclient-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer
&client_assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRw
czovL2p3dC1pZHAuZXhhbXBsZS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiJtYWlsdG86bWlrZUBleGFtcGxlLmN
vbSIsIm5iZiI6MTQ5OTE4MzYwMSwiZXhwIjoxNDk5MTg3MjAxLCJpYXQiOjE0OTkxODM2MD
EsImp0aSI6ImlkMTIzNDU2IiwidHlwIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9leGFtcGxlLmNvbS9yZWdpc3Rlc
iJ9.SAxPMaJK_wYl_W2idTQASjiEZ4UoI7-P2SbmnHKr6LvP8ZJZX6JlnpK_xClJswAni1T
p1UnHJslc08JrexctaeEIBrqwHG18iBcWKjhHK2Tv5m4nbTsSi1MFQOlMUTRFq3_LQiHqV2
M8Hf1v9q9YaQqxDa4MK0asDUtE_zYMHz8kKDb-jj-Vh4mVDeM4_FPiffd2C5ckjkrZBNOK0
01Xktm7xTqX6fk56KTrejeA4x6D_1ygJcGfjZCv6Knki7Jl-6MfwUKb9ZoZ9LiwHf5lLXPuy
_QrOyM0pONWKj9K4Mj7I4GPGvzyVqpaZUgjcOaZY_rlu_p9tnSlE781dDLuw
Non-Base64 JWT client_assertion {
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": "12345",
"typ": "JWT"
}
.
{
"iss": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"sub": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"exp": 1499187201,
"iat": 1499183601,
"jti": "id123456",
"aud": "https://authn.alphabank.com/as/token.oauth2"
}
.
<<signature>>
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
Pragma: no-cache
{
"access_token": "SlAV32hkKG",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3600
}
|
Step 4 - Create Payment-Submission
1. The PISP has an Access Token which can be used to Create a Payment-Submission (Step 4). The PISP must obtain the PaymentId (Intent-ID) so that the Payment request is associated with the correct PaymentId. This can be sourced from either:
- The PaymentId claim from the signed ID Token (default). The PISP will need to decode the ID Token JWT and locate the claim attribute associated with the PaymentId.
- The PaymentId claim from the /userInfo resource endpoint of the ASPSP (optional for ASPSPs to implement) .
The example below provides an illustration of the PISP requesting the /userInfo endpoint of the ASPSP in order to get the PaymentID (returned as openbanking_intent_id)
| Request : UserInfo | Response : UserInfo |
|---|---|
GET /userinfo HTTP/1.1 Host: api.alphabank.com Authorization: Bearer SlAV32hkKG | HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"sub": "PSU User Id",
"openbanking_intent_id": [ "IntentId:1", "IntentId:2" ],
"name": "Open Banking",
"given_name": "Open Banking",
"family_name": "Open Banking",
"preferred_username": "Open Banking",
"email": "Open Banking@example.com",
"picture": "http://example.com/janedoe/me.jpg"
}
|
2. The PISP can now invoke the /payment-submissions endpoint to commit the Payment using the Access Token and PaymentId in the payload of the request. This example is sourced from the Payment Initiation API Specification
| Request : payment-submissions | Response : payment-submissions |
|---|---|
POST /payment-submissions HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer SlAV32hkKG
x-idempotency-key: FRESNO.1317.GFX.22
x-fapi-financial-id: OB/2017/001
x-fapi-customer-last-logged-time: 2017-06-13T11:36:09
x-fapi-customer-ip-address: 104.25.212.99
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: application/json
{
"Data": {
"PaymentId": "58923",
"Initiation": {
"InstructionIdentification": "ACME412",
"EndToEndIdentification": "FRESCO.21302.GFX.20",
"InstructedAmount": {
"Amount": "165.88",
"Currency": "GBP"
},
"CreditorAccount": {
"SchemeName": "SortCodeAccountNumber",
"Identification": "08080021325698",
"Name": "ACME Inc",
"SecondaryIdentification": "0002"
},
"RemittanceInformation": {
"Reference": "FRESCO-101",
"Unstructured": "Internal ops code 5120101"
}
}
},
"Risk": {
"PaymentContextCode": "EcommerceGoods",
"MerchantCategoryCode": "5967",
"MerchantCustomerIdentification": "053598653254",
"DeliveryAddress": {
"AddressLine": [
"Flat 7",
"Acacia Lodge"
],
"StreetName": "Acacia Avenue",
"BuildingNumber": "27",
"PostCode": "GU31 2ZZ",
"TownName": "Sparsholt",
"CountySubDivision": [
"Wessex"
],
"Country": "UK"
}
}
}
| HTTP/1.1 201 Created
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Data": {
"PaymentSubmissionId": "58923-001",
"PaymentId": "58923",
"Status": "AcceptedSettlementInProcess",
"CreationDateTime": "2017-06-05T15:15:22+00:00"
},
"Links": {
"Self": "https://api.alphabank.com/open-banking/v1.0/payment-submissions/58923-001"
},
"Meta": {}
}
|
Step 5 - Get Payment-Submission Status
1. The PISP can query for the status of a Payment-Submission by invoking the /payment-submissions using the known PaymentSubmissionId. This can use an existing access token with payments scope or the PISP can obtain a fresh access token by replaying the client credentials grant request as per Step 2 - Setup Single Payment Initiation.
| Request: payment-submissions/{PaymentSubmissionId} | Response: payment-submissions |
|---|---|
GET /payment-submissions/58923-001 HTTP/1.1 Authorization: Bearer SlAV32hkKG x-fapi-financial-id: OB/2017/001 x-fapi-customer-last-logged-time: 2017-06-13T11:36:09 x-fapi-customer-ip-address: 104.25.212.99 x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d Accept: application/json | HTTP/1.1 200 OK
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Data": {
"PaymentSubmissionId": "58923-001",
"PaymentId": "58923",
"Status": "AcceptedSettlementInProcess",
"CreationDateTime": "2017-06-05T15:15:22+00:00"
},
"Links": {
"Self": "https://api.alphabank.com/open-banking/v1.0/payment-submissions/58923-001"
},
"Meta": {}
}
|
2. A PISP can also optionally query for the status of a Payment resource by invoking /payments/{PaymentId}. This can use an existing access token with payments scope or the PISP can obtain a fresh access token by replaying the client credentials grant request as per Step 2 - Setup Single Payment Initiation.
Account API Specification
The sequence diagram below highlights the OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials Grant and OIDC Hybrid flow that are used by the Account and Transactions API.
Client Credentials Grant Type (OAuth 2.0)
Summary
This grant type is used by the AISP in Step 2 to register an intent for the PSU to allow the AISP to retrieve their Account information from an ASPSP.
- The AISP initiates an Authorization request using valid Client Credentials Grant type and scope(s)
- The ASPSP Authorization Server validates the Client Authentication request from the AISP and generates an Access Token response where the request is valid
- The AISP uses the Access Token to create a new Account Request resource against the ASPSP Resource Server
- The ASPSP Resource server responds with the AccountRequestId representing the resource it has created.
OIDC Hybrid Flow
Summary
- This is initiated at the end of Step 2 by the AISP after the AccountRequestId is generated by the ASPSP and returned to the AISP.
- This is used in a redirect across the PSU and ASPSP in Step 3 in order for the PSU to authorize consent with the ASPSP - for the AISP to proceed with the requesting Account information.
- This is used across the AISP and ASPSP in Step 4 by swapping the Authorization Code for an Access Token in order to retrieve PSU Account information.
Non-Normative HTTP Request and Response Examples
Step 1 - Request Account Information
There are no Requests and Responses against the Payments API in this Step for the PSU, PISP and ASPSP.
Step 2 - Setup Account Request
1. AISP obtains an Access Token using a Client Credentials Grant Type. The scope accounts must be used. When an Access Token expires, the AISP will need to re-request for another Access Token using the same request below.
Request : Client Credentials using private_key_jwt | Response : Client Credentials |
|---|---|
POST /as/token.oauth2 HTTP/1.1 Host: https://authn.alphabank.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Accept: application/json grant_type=client_credentials &scope=accounts &client-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer &client_assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRw czovL2p3dC1pZHAuZXhhbXBsZS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiJtYWlsdG86bWlrZUBleGFtcGxlLmN vbSIsIm5iZiI6MTQ5OTE4MzYwMSwiZXhwIjoxNDk5MTg3MjAxLCJpYXQiOjE0OTkxODM2MD EsImp0aSI6ImlkMTIzNDU2IiwidHlwIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9leGFtcGxlLmNvbS9yZWdpc3Rlc iJ9.SAxPMaJK_wYl_W2idTQASjiEZ4UoI7-P2SbmnHKr6LvP8ZJZX6JlnpK_xClJswAni1T p1UnHJslc08JrexctaeEIBrqwHG18iBcWKjhHK2Tv5m4nbTsSi1MFQOlMUTRFq3_LQiHqV2 M8Hf1v9q9YaQqxDa4MK0asDUtE_zYMHz8kKDb-jj-Vh4mVDeM4_FPiffd2C5ckjkrZBNOK0 01Xktm7xTqX6fk56KTrejeA4x6D_1ygJcGfjZCv6Knki7Jl-6MfwUKb9ZoZ9LiwHf5lLXPuy _QrOyM0pONWKj9K4Mj7I4GPGvzyVqpaZUgjcOaZY_rlu_p9tnSlE781dDLuw Non-Base64 JWT client_assertion {
"alg": "RS256",
"typ": "JWT",
"kid": "1234adsf"
}
.
{
"iss": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"sub": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"exp": 1499187201,
"iat": 1499183601,
"jti": "id123456",
"aud": "https://authn.alphabank.com/as/token.oauth2"
}
.
<<signature>>
| Content-Length: 1103
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Mon, 26 Jun 2017 15:18:28 GMT
{
"access_token": "2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA",
"expires_in": 3600,
"token_type": "bearer",
"scope":"accounts"
}
|
2. AISP uses the Access Token (with accounts scope) from the ASPSP to invoke the Accounts API. This example is sourced directly from the Account and Transactions API Specification
| Request: Accounts API | Response: Accounts API |
|---|---|
POST /account-requests HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer 2YotnFZFEjr1zCsicMWpAA
x-fapi-financial-id: OB/2017/001
x-fapi-customer-last-logged-time: 2017-06-13T11:36:09
x-fapi-customer-ip-address: 104.25.212.99
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: application/json
{
"Data": {
"Permissions": [
"ReadAccountsDetail",
"ReadBalances",
"ReadBeneficiariesDetail",
"ReadDirectDebits",
"ReadProducts",
"ReadStandingOrdersDetail",
"ReadTransactionsCredits",
"ReadTransactionsDebits",
"ReadTransactionsDetail"
],
"ExpirationDateTime": "2017-05-02T00:00:00+00:00",
"TransactionFromDateTime": "2017-05-03T00:00:00+00:00",
"TransactionToDateTime": "2017-12-03T00:00:00+00:00"
},
"Risk": {}
}
| HTTP/1.1 201 Created
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Data": {
"AccountRequestId": "88379",
"Status": "AwaitingAuthorisation",
"CreationDateTime": "2017-05-02T00:00:00+00:00",
"Permissions": [
"ReadAccountsDetail",
"ReadBalances",
"ReadBeneficiariesDetail",
"ReadDirectDebits",
"ReadProducts",
"ReadStandingOrdersDetail",
"ReadTransactionsCredits",
"ReadTransactionsDebits",
"ReadTransactionsDetail"
],
"ExpirationDateTime": "2017-08-02T00:00:00+00:00",
"TransactionFromDateTime": "2017-05-03T00:00:00+00:00",
"TransactionToDateTime": "2017-12-03T00:00:00+00:00"
},
"Risk": {},
"Links": {
"Self": "/account-requests/88379"
},
"Meta": {
"TotalPages": 1
}
}
|
Step 3 - Authorize Consent
1. AISP receives a AccountRequestId from the ASPSP. The AISP then creates an Authorization request (using a signed JWT Request containing the AccountRequestId as a claim) for the PSU to consent to the Account request directly with their ASPSP. The request is an OIDC Hybrid flow (requesting for Code and id_token)
Request : OIDC Hybrid Flow | Response : OIDC Hybrid Flow |
|---|---|
|
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location: https://api.mytpp.com/cb#
code=SplxlOBeZQQYbYS6WxSbIA
&id_token=eyJ0 ... NiJ9.eyJ1c ... I6IjIifX0.DeWt4Qu ... ZXso
&state=af0ifjsldkj
|
2. The PSU is then redirected to the AISP. The AISP will now possess the Authorization Code and ID Token from the ASPSP. Note at this point, there is no Access Token. The AISP will now introspect the ID Token and use it as a detached signature to check:
- The hash of the Authorization Code to prove it hasn't been tampered with during redirect (comparing the hash value against the c_hash attribute in ID Token)
- The hash of the State to prove it hasn't been tampered with during redirect (comparing the state hash value against the s_hash attribute in the ID Token)
Example: ID Token |
|---|
|
3. Once the state and code validations have been confirmed as successful by use of the ID token, the AISP will proceed to obtain an Access Token from the ASPSP using the Authorization Code they now possess. The AISP will present its Authorization Code together with the private_key_jwt. The Access Token is required by the AISP in order to access PSU Account information. The accounts scope should already be associated with the Authorization Code generated in the previous step.
Request : Access Token request using Authorization Code and private_key_jwt | Response : Access Token (with Optional Refresh Token) |
|---|---|
POST /as/token.oauth2 HTTP/1.1 Host: https://authn.alphabank.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Accept: application/json grant_type=authorization_code &redirect_uri=https://api.mytpp.com/cb &code=SplxlOBeZQQYbYS6WxSbIA &client-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer &client_assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRw czovL2p3dC1pZHAuZXhhbXBsZS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiJtYWlsdG86bWlrZUBleGFtcGxlLmN vbSIsIm5iZiI6MTQ5OTE4MzYwMSwiZXhwIjoxNDk5MTg3MjAxLCJpYXQiOjE0OTkxODM2MD EsImp0aSI6ImlkMTIzNDU2IiwidHlwIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9leGFtcGxlLmNvbS9yZWdpc3Rlc iJ9.SAxPMaJK_wYl_W2idTQASjiEZ4UoI7-P2SbmnHKr6LvP8ZJZX6JlnpK_xClJswAni1T p1UnHJslc08JrexctaeEIBrqwHG18iBcWKjhHK2Tv5m4nbTsSi1MFQOlMUTRFq3_LQiHqV2 M8Hf1v9q9YaQqxDa4MK0asDUtE_zYMHz8kKDb-jj-Vh4mVDeM4_FPiffd2C5ckjkrZBNOK0 01Xktm7xTqX6fk56KTrejeA4x6D_1ygJcGfjZCv6Knki7Jl-6MfwUKb9ZoZ9LiwHf5lLXPuy _QrOyM0pONWKj9K4Mj7I4GPGvzyVqpaZUgjcOaZY_rlu_p9tnSlE781dDLuw Non-Base64 JWT client_assertion {
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": "12345",
"typ": "JWT"
}
.
{
"iss": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"sub": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"exp": 1499187201,
"iat": 1499183601,
"jti": "id123456",
"aud": "https://authn.alphabank.com/as/token.oauth2"
}
.
<<signature>>
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
Pragma: no-cache
{
"access_token": "SlAV32hkKG",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3600,
"refresh_token": "1Sm4HAl33z4"
}
|
Step 4 - Request Account Data
1. The AISP can use the Access Token to retrieve Accounts (bulk or specific). The following examples are from the Account and Transaction API Specification
Where the initial Access Token expires, the AISP can use the Refresh token in order to obtain a fresh Access Token.
| Request : Accounts API | Response: Accounts API |
|---|---|
Example request against the bulk Accounts resource GET /accounts HTTP/1.1 Authorization: Bearer SlAV32hkKG x-fapi-financial-id: OB/2017/001 x-fapi-customer-last-logged-time: 2017-06-13T11:36:09 x-fapi-customer-ip-address: 104.25.212.99 x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d Accept: application/json | HTTP/1.1 200 OK
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Data": {
"Account": [
{
"AccountId": "22289",
"Currency": "GBP",
"Nickname": "Bills",
"Account": {
"SchemeName": "SortCodeAccountNumber",
"Identification": "80200110203345",
"Name": "Mr Kevin",
"SecondaryIdentification": "00021"
}
},
{
"AccountId": "31820",
"Currency": "GBP",
"Nickname": "Household",
"Account": {
"SchemeName": "SortCodeAccountNumber",
"Identification": "80200110203348",
"Name": "Mr Kevin"
}
}
]
},
"Links": {
"Self": "/accounts/"
},
"Meta": {
"TotalPages": 1
}
}
|
Example request for a specific Account Id GET /accounts/22289 HTTP/1.1 Authorization: Bearer SlAV32hkKG x-fapi-financial-id: OB/2017/001 x-fapi-customer-last-logged-time: 2017-06-13T11:36:09 x-fapi-customer-ip-address: 104.25.212.99 x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d Accept: application/json | HTTP/1.1 200 OK
x-fapi-interaction-id: 93bac548-d2de-4546-b106-880a5018460d
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Data": {
"Account": [
{
"AccountId": "22289",
"Currency": "GBP",
"Nickname": "Bills",
"Account": {
"SchemeName": "SortCodeAccountNumber",
"Identification": "80200110203345",
"Name": "Mr Kevin",
"SecondaryIdentification": "00021"
}
}
]
},
"Links": {
"Self": "/accounts/22289"
},
"Meta": {
"TotalPages": 1
}
}
|
| Request: Refresh Token request using private_key_jwt | Response: Refresh Token |
POST /as/token.oauth2 HTTP/1.1 Host: https://authn.alphabank.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Accept: application/json grant_type=refresh_token &refresh_token=1Sm4HAl33z4 &scope=openid accounts &client-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer &client_assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRw czovL2p3dC1pZHAuZXhhbXBsZS5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiJtYWlsdG86bWlrZUBleGFtcGxlLmN vbSIsIm5iZiI6MTQ5OTE4MzYwMSwiZXhwIjoxNDk5MTg3MjAxLCJpYXQiOjE0OTkxODM2MD EsImp0aSI6ImlkMTIzNDU2IiwidHlwIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9leGFtcGxlLmNvbS9yZWdpc3Rlc iJ9.SAxPMaJK_wYl_W2idTQASjiEZ4UoI7-P2SbmnHKr6LvP8ZJZX6JlnpK_xClJswAni1T p1UnHJslc08JrexctaeEIBrqwHG18iBcWKjhHK2Tv5m4nbTsSi1MFQOlMUTRFq3_LQiHqV2 M8Hf1v9q9YaQqxDa4MK0asDUtE_zYMHz8kKDb-jj-Vh4mVDeM4_FPiffd2C5ckjkrZBNOK0 01Xktm7xTqX6fk56KTrejeA4x6D_1ygJcGfjZCv6Knki7Jl-6MfwUKb9ZoZ9LiwHf5lLXPuy _QrOyM0pONWKj9K4Mj7I4GPGvzyVqpaZUgjcOaZY_rlu_p9tnSlE781dDLuw | A new Access Token and Refresh Token will be returned to the AISP for them to query /accounts resources HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
Pragma: no-cache
{
"access_token": "TYstftas123j",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3600,
"refresh_token": "XUUGas123ed"
}
|
Edge Cases
This section provides further information on potential edge cases that may arise via the implementation of Accounts and Payments API Specifications.
PSU Consent Authorization Interrupt with ASPSP
| API | Scenario | Workflow Step | Impact | Solution Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Payments | Due to an interruption, the PSU does not complete the Authorization of the Payment with the ASPSP when redirected by the PISP (after creating a PaymentId) | Step 3: Authorize Consent | Payment Status remains as Pending or AcceptedTechnicalValidation | The PISP may choose to implement a separate follow up process which reminds the PSU to complete their Authorization consent steps with the ASPSP. This would imply re-using the PaymentId that has a status of Pending or AcceptedTechnicalValidation and re-issuing another Hybrid Flow request to the ASPSP. The implementation of how the follow up process is initiated is in the competitive space for the PISPs to decide. |
| Accounts | Due to an interruption, the PSU does not complete the Authorization of the Accounts request with the ASPSP when redirected by the AISP (after creating an AccountRequestId) | Step 3: Authorize Consent | Account Status remains as AwaitingAuthorisation | The AISP may choose to implement a separate follow up process which reminds the PSU to complete their Authorization consent steps with the ASPSP. This would imply re-using the AccountRequestId that has a status of AwaitingAuthorisation and re-issuing another Hybrid Flow request to the ASPSP. The implementation of how the follow up process is initiated is in the competitive space for the AISPs to decide. |
© Open Banking Limited 2019 | https://www.openbanking.org.uk/open-licence | https://www.openbanking.org.uk
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1515410935149&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=900&height=2227)
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1515410934937&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=900&height=2789)